Gwalior
- Gwalior is a city in Madhya Pradesh, India, lying 76 miles (122 km) south of Agra, and known as the tourist capital of Madhya Pradesh.
- Gwalior occupies a strategic location in the Gird region of India, and the city and its fortress have served as the center of several of historic northern Indian kingdoms.
- That the location of the city still is considered militarily important is signaled by the presence of a major air force base at Maharajpura.
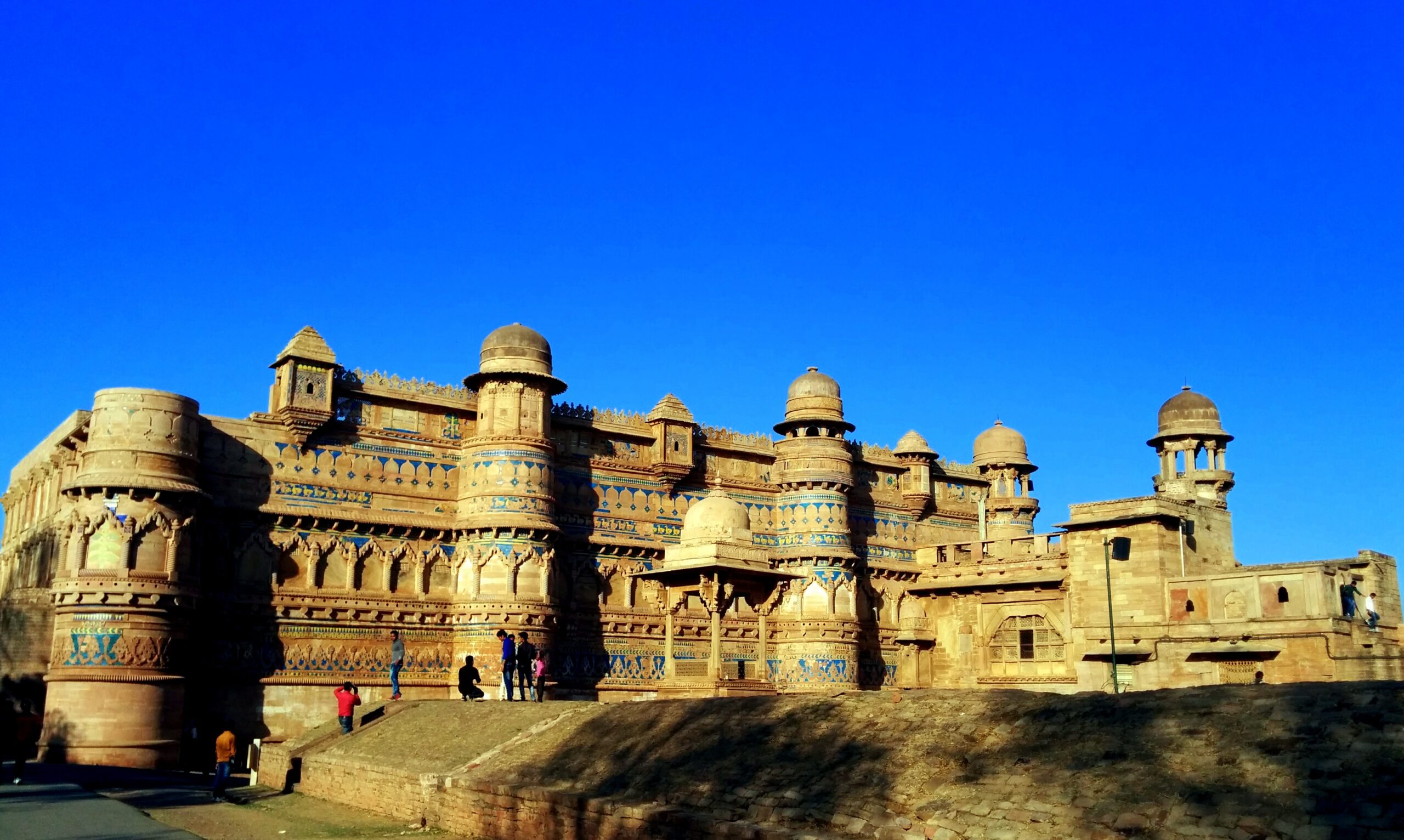

- According to local tradition, Gwalior owes its name to a sage of former times. SurajSen, a prince of the Kachhwaha clan of the eighth century, is said to have lost his way in the jungle.
- On a secluded hill he met an old man, the sage Gwalipa, whose influence almost took him by surprise. Upon asking the sage for some drinking water he was led to a pond; the waters not only quenched his thirst but cured him of leprosy.
- Out of gratefulness, the prince wished to offer the sage something in return, and the sage asked him to build a wall on the hill in order to protect the other sages from wild animals which often disturbed their yagnas (or pujas).
- SurajSen later built a palace inside the fort, which had been named "Gwalior" after the sage; eventually the city which grew around the fort took the same name.
- Gwalior is well connected by train services to all parts of the country, including 4 metros. There are direct trains to Mumbai, Delhi, Kolkata (Howrah), Chennai, Trivandrum, Indore, Jaipur, Udaipur, Ahmedabad, Pune, Jammu, Lucknow, Bhopal, Bangalore and other major towns.
- Gwalior is the main station serving most of the important and long distance trains. Gwalior lies on the longest functional broad gauge line in India between Delhi and Mumbai.
Trips
& tours
Choose M.P Holidays®
- Approved by “The Ministry of Tourism” (Approval No: 2203270HE874)
- “The Official No.1 Channel Partner” of M.P Tourism (Registration No: MP-TOUR-20221/131888)
- We are Awarded “The Best Travel Agent” by M.P. Government for the three consecutive years. (2016, 2017 and 2018)
- Having offices at
- Surat
- Indore
- Ahmedabad
- Pachmarhi
- Nagpur
- Kanha
- Discover Madhya Pradesh from major cities like Surat, Ahmedabad, Delhi, Mumbai, Nagpur, Pune and beyond—experience the best of India, no matter where you start.
- Own resort at Madhya Pradesh.